flexFitR is an R package designed for efficient modeling and analysis of large and complex datasets. It offers powerful tools for parameter estimation, model fitting, and visualization, leveraging the optimx package for optimization and the future package for parallel processing.
Installation
Install released version from CRAN:
install.packages("flexFitR")You can also install the development version of flexFitR from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("AparicioJohan/flexFitR")Features
- Parameter Estimation: Utilizes optimx algorithms to solve and estimate parameters for a given function.
- Parallelization: Implements parallel processing using the future package, enabling efficient fitting of hundreds of curves simultaneously.
- Visualization Tools: Provides a variety of plots to visualize model fits, correlations, predictions, derivatives, and more.
- Statistical Rigor: Offers standard errors and p-values for coefficients, as well as for predictions, supporting robust conclusions and interpretations.
- Prediction: Supports diverse prediction types, including point predictions, area under the curve (AUC), first and second derivatives, and custom expressions based on model parameters.
- Flexibility: Allows users to fix certain parameters in the model and specify different initial values per grouping factor, accepting both numerical inputs and expressions.
- Custom Modeling Functions: Equipped with built-in modeling functions for common analysis tasks, while also permitting users to supply their own custom functions.
Example
Here’s a simple example to get you started with flexFitR. This example demonstrates fitting a piecewise regression model:
library(flexFitR)
dt <- data.frame(
time = c(0, 29, 36, 42, 56, 76, 92, 100, 108),
variable = c(0, 0, 0.67, 15.11, 77.38, 99.81, 99.81, 99.81, 99.81)
)
plot(explorer(dt, time, variable), type = "xy")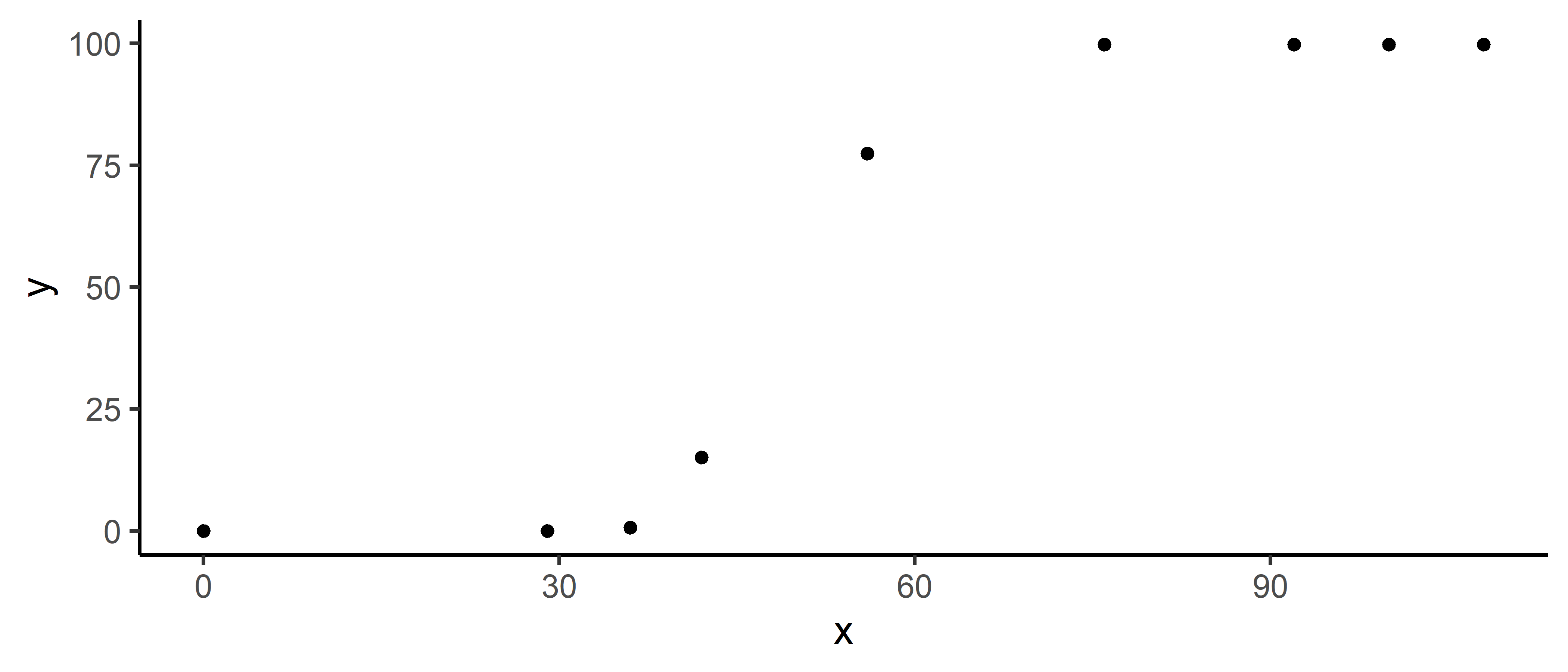
fn_lin_plat <- function(t, t1 = 45, t2 = 80, k = 0.9) {
ifelse(
test = t < t1,
yes = 0,
no = ifelse(t >= t1 & t <= t2, k / (t2 - t1) * (t - t1), k)
)
}
# Fitting a linear plateau function
mod_1 <- dt |>
modeler(
x = time,
y = variable,
fn = "fn_lin_plat",
parameters = c(t1 = 45, t2 = 80, k = 90)
)print(mod_1)
Call:
variable ~ fn_lin_plat(time, t1, t2, k)
Residuals (`Standardized`):
Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.2722 0.0000 2.4495
Optimization Results `head()`:
uid t1 t2 k sse
1 38.6 61 99.8 0.449
Metrics:
Groups Timing Convergence Iterations
1 0.1081 secs 100% 511 (id)
# Auto plot
plot(mod_1)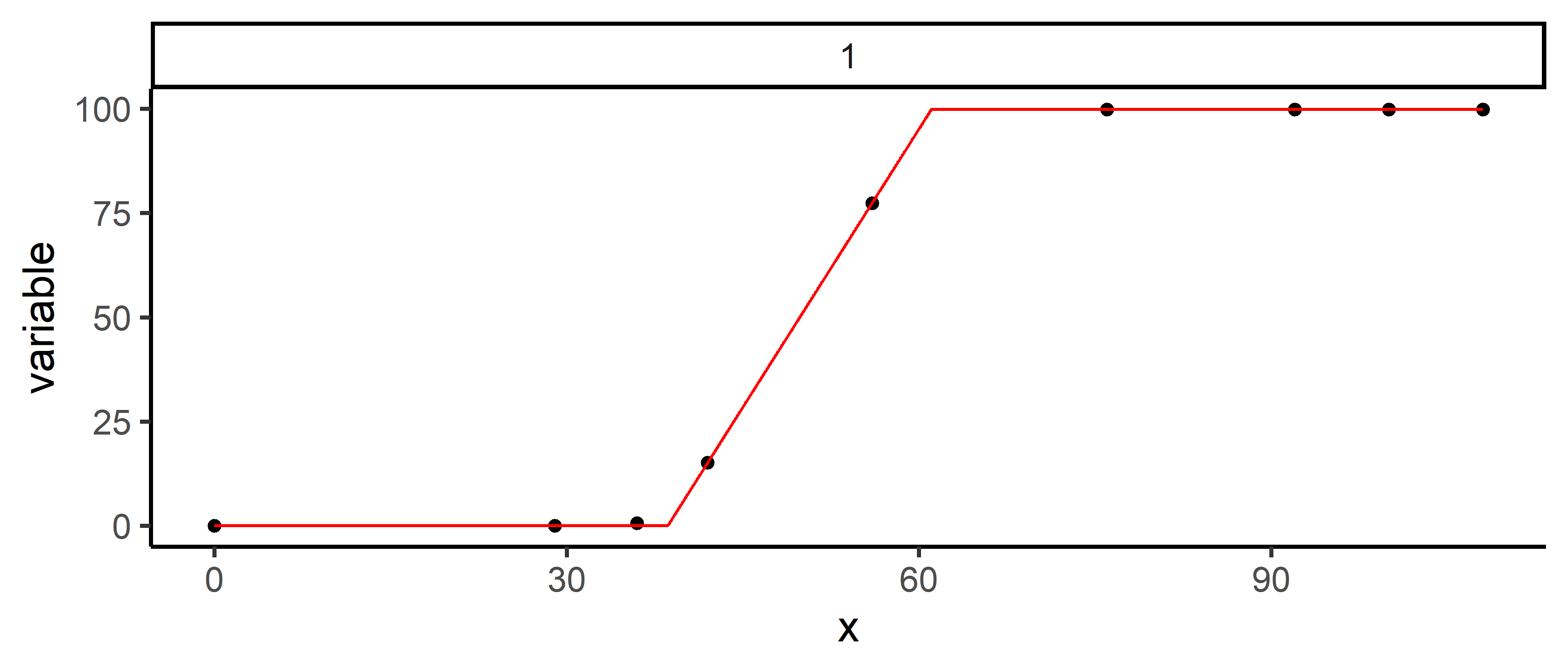
# Coefficients
coef(mod_1)
# A tibble: 3 × 7
uid fn_name coefficient solution std.error `t value` `Pr(>|t|)`
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 fn_lin_plat t1 38.6 0.0779 496. 4.54e-15
2 1 fn_lin_plat t2 61.0 0.0918 665. 7.82e-16
3 1 fn_lin_plat k 99.8 0.137 730. 4.47e-16Documentation
For detailed documentation and examples, visit flexFitR
- Vignette 1: How to start
- Vignette 2: Modeling plant emergence and canopy growth using UAV data
- Vignette 3: Modeling with constraints
- Vignette 4: Making predictions
- Vignette 5: Plotting options
Contributing
Contributions to flexFitR are welcome! If you’d like to contribute, please fork the repository and submit a pull request. For significant changes, please open an issue first to discuss your ideas.
Code of Conduct
Please note that the flexFitR project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
License
flexFitR is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.
